
Sustainability
Prosper Together - we are focused on making a positive impact on society and our shared planet through all our corporate activities so that everyone may prosper together.
We aim to create a world where people are driven by their passion. The growth and future of our business will be powered by people, technology, and an investment in the longevity of our society and the environment.
Hisayuki “Deko” Idekoba
Representative Director, President and
CEO
Recruit Holdings
Message from Our Leaders
Our ESG Commitment to 2030
-

Environmental

Greenhouse gas emissions*2
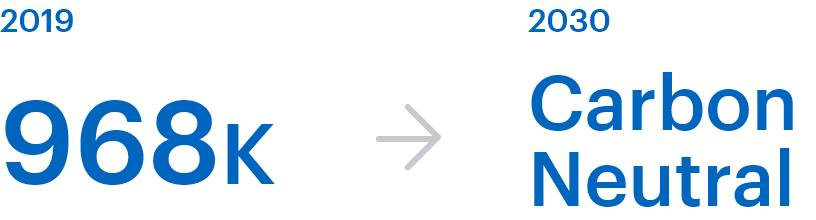
Achieving carbon neutrality in greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) across our entire value chain by FY2030*2.
-

Social

Time it takes to get hired*3

Reducing the time it takes to get hired by half by FY2030 compared to that of FY2021*3.
-

Job seekers facing barriers*4
Helping 30 million people facing barriers in the labor market around the world get hired ― barriers such as education, disabilities, criminal records, experience in military services and others*4.
-

Women's representation in leadership

Achieving gender parity among senior executives, those in managerial positions, and all employee levels by FY2030 at Recruit Group*5.
-

Governance

Board gender diversity*6

Achieving gender parity among the members of the Board of Directors and Audit & Supervisory Board of Recruit Holdings by FY2030*6.
Our Journey to 2030
-
Announced our progress in FY2021
- E: Achieved carbon neutrality in our own business activities and set a three-year reduction target for GHG emissions
- S-Impact: Calculated the baseline job search duration as 15 weeks
- S-Impact: Supported job seekers facing barriers that can lead to prolonged unemployment
- S: Set a three-year target toward achieving gender parity across our employee base
- G: Increased the percentage of women on the Board of Directors from 20% to approximately 27%, and set a three-year goal toward achieving gender parity
-
Announced the progress for FY2022
- E: Achieved carbon neutrality in our business operations for two consecutive years. Received validation by SBTi on our GHG reduction target
- S-Impact: Improved our products to reduce the time to get hired and deepened our analysis of user data
- S-Impact: Focused on reducing the five barriers (education, criminal records, disability, prior military service experience, and lack of work essentials) that cause prolonged periods of unemployment and advanced toward our goal by helping 3.9 million job seekers facing barriers get hired
- S: Advanced our initiatives to achieve the three-year target
- G: Increased women's representation among the members of the Board to approximately 33%. Linked the achievement of three-year targets to a portion of long-term incentive compensation
- On this webpage, the number of years stated are reflective of the number of Recruit Holdings fiscal years which begin on April 1 each year and end March 31 of the following year. All figures displayed here are approximate.
- GHG emissions throughout our business activities are the sum of direct emissions from the use of fuels in owned or controlled sources and are referred to as Scope 1. Indirect emissions from the use of purchased electricity, heat, or steam in owned or controlled sources are referred to as Scope 2. GHG emissions from the value chain are referred to as Scope 3, and comprise indirect emissions other than Scope 1 and 2. The entire value chain represents the sum of Scopes 1, 2 and 3 GHG emissions. The Company aims to achieve carbon neutrality upon completion of the following steps: measurement of GHG emissions, obtaining an accredited third-party assurance on the amount of GHG emissions, and offsetting of those emissions.
- The period from the time a user starts an active job search on the Indeed job platform to the time the user confirms receipt of a job offer.
- The initiative as of today includes providing assistance through the Company's online job platform, and through partnerships with NPOs and other organizations with whom the Company collaborates. The Company may also aim to reduce other various barriers, including newly emerging issues in the labor market by FY2030.
- Senior executive positions are defined as Senior Vice Presidents and Corporate Officers of Recruit Holdings and Matching & Solutions Strategic Business Unit (SBU), and CEOs of the Company's major subsidiaries and heads of key functions in the HR Technology and Staffing SBUs. Figures for managerial positions and employees are calculated from Recruit Holdings, SBU Headquarters, and primary operating companies of each SBU. Managerial positions mean all of those that have subordinate employees.
- The Board of Directors members are defined as directors of the Board and Audit & Supervisory Board members.



